Download
STABLE RELEASE
ESP32forth-7.0.6.19.zip
- Single .ino file ready for installation
Version: 7.0.6.19 (Stable)
LONG TERM STABLE RELEASE
ESP32forth-7.0.5.4.zip
- Single .ino file ready for installation
Version: 7.0.5.4 (Long-term Stable)
Beta Release
ESP32forth-7.0.7.22.zip
- Single .ino file ready for installation
Version: 7.0.7.22 (Beta)
Release Archive - Prior Releases
http://github.com/flagxor/ueforth - Complete Unprocessed Source Code
License
NOTE: Although Esp32forth is licensed under Apache 2.0,
please be aware that binaries built with the Arduino IDE (such as ESP32forth) include
components and libraries under
other additional licenses.
The ESP32 plugin for Arduino is also under a
different license.
Additionally, the ESP32 toolchain used by Arduino, contains further components under
other licenses.
Be sure to consult a lawyer before using for comercial purposes.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Install
Download the Arduino IDE for your platform.
Go to File > Preferences.
Under Additional Board Manager URLs add:
- For ESP32 -
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json - For ESP32-S2 or ESP32-C3 -
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/gh-pages/package_esp32_dev_index.json
Select your serial port under Tools > Port.
Under Tools choose board and settings as below under Tools.
Use
Initially ESP32forth can be interacted with over a serial port (over USB).
You can do this from the Arduino IDE's Serial Monitor option.
Be sure to config the serial port to: baud rate = 115200, data bits = 8, stop bits = 1, and parity = N.
On boot, ESP32forth configures PIN 2 (typically an LED) to be an output and brings it HIGH (lighting the LED after boot).
ESP32forth Features
ESP32forth Specific Words
Null Terminated Strings
As null terminated strings are used throughout C interfaces, their use is supported in Forth by way of several non-standard words with the convention of using Z/z to refer to such strings in names and stack comments.
Z" ( "string" -- z ) Creates a null terminated string on the heap Z>S ( z -- a n ) Convert a null terminated string to a counted string S>Z ( a n -- z ) Conver a counted string string to null terminated (copies string to heap)
Raw Strings
Raw strings are provided better support using a string for the duration of the current command, without consuming heap memory.
R" ( "string" -- a n ) Creates a temporary counted string R| ( string| -- a n ) Creates a temporary counted string ending with |
Utilities
DUMP ( a n -- ) Dump a memory region SEE ( "name" -- ) Attempt to decompile a word VARIABLE ECHO -- Determines if commands are echoed REMAINING ( -- n ) Bytes remaining in Forth heap. DUMP-FILE ( data data# fn fn# -- ) Write contents of a file throws on error.
Vocabularies
ESP32forth uses a hybrid of Forth-79 and Forth-83 style vocabularies.
By default vocabularies chain to the vocabulary in which they were defined,
as in Forth-79. However, like Forth-83, ALSO
can be used to add vocabularies to a vocabulary stack of which
CONTEXT @ is the first item.
The word ONLY clears the vocabulary stack, but as there is
no separate ONLY vocabulary, it also sets CONTEXT
to the FORTH vocabulary.
The word SEALED modifies the most recently defined vocabulary
such that it does not chain. Note, this must be done before words are added to it.
VOCABULARY ( "name" ) Create a vocabulary with the current vocabulary as parent
FORTH ( -- ) Make the FORTH vocabulary the context vocabulary
DEFINITIONS ( -- ) Make the context vocabulary the current vocabulary
VLIST ( -- ) List the words in the context vocabulary (not chains)
WORDS ( -- ) List the words in the context vocabulary (including chains)
TRANSFER ( "name" ) Move a word from its current dictionary to the current vocabulary
Useful for "hiding" built-in words
TRANSFER{ ..words.. }TRANSFER ( -- ) Transfer multiple words to the current vocabulary
ALSO ( -- ) Duplicate the vocabulary at the top of the vocabulary stack
PREVIOUS ( -- ) Drop the vocabulary at the top of the vocabulary stack
ONLY ( -- ) Reset context stack to one item, the FORTH dictionary
Non-standard, as there's no distinct ONLY vocabulary
ORDER ( -- ) Print the vocabulary search order
SEALED ( -- ) Alter the last vocabulary defined so it doesn't chain
Interpret Time Conditions
[IF], [ELSE], and [THEN] can be used
to selectively compile. Used in tandem with DEFINED? they can
be used to handle the absence of modules gracefully.
Nesting is supported.
DEFINED? ( "name" -- xt|0 ) Check if a word exists (works at compile time too). [IF] ( f -- ) Conditionally interpret the text the follows. [ELSE] ( -- ) Interpret time ELSE. [THEN] ( -- ) Interpret time THEN.
Floating-Point
Requires v7.0.6.5+
Single precision floating-point support is available as a work in progress. While initially left out in the name of minimalism, hardware support for floating-point argues some advantages to limited support.
Floating point is kept on a separate stack.
NOTE: Tasks currently don't correctly support floating point. A single floating point stack is shared by all tasks.
FLOAT OPCODES ------------- DOFLIT ( --- ) Puts a float from the next cell onto float stack. FP@ ( -- a ) FP! ( a -- ) SF@ ( a -- r ) Single precision load SF! ( r a -- ) Single precision store FDUP ( r -- r r ) FNIP ( ra rb -- rb ) FDROP ( r -- ) FOVER ( ra rb -- ra rb ra ) FSWAP ( ra rb -- rb ra ) F0< ( r -- f ) F0= ( r -- f ) F+ ( r r -- r ) F- ( r r -- r ) F* ( r r -- r ) F/ ( r r -- r ) 1/F ( r -- r ) S>F ( n -- r ) F>S ( r -- n ) HIGH LEVEL ---------- F= ( r r -- f ) F< ( r r -- f ) F> ( r r -- f ) F<= ( r r -- f ) F>= ( r r -- f ) F<> ( r r -- f ) SFLOAT ( -- 4 ) SFLOATS ( n -- n*4 ) SFLOAT+ ( a -- a+4 ) SF, ( r -- ) AFLITERAL ( r -- ) FLITERAL ( r -- ) IMMEDIATE FCONSTANT ( r "name" ) FVARIABLE ( "name" ) PI ( -- r ) FSQRT ( r r -- r ) F.S ( -- ) Print float stack.
Locals
Locals allow named word local parameters and values.
Syntax:
{ local1 local2 .. -- comment }
or
{ local1 local2 .. }
Locals are ordered to match the stack, examples:
: 2OVER { a b c d } a b c d a b ;
: MAX { a b -- biggest } a b < IF b ELSE a THEN ;
( Equivalent with DO and FOR )
: POW2 { n } 1 { s } n FOR AFT s 2* to s THEN NEXT s ;
: POW2 { n } 1 { s } n 0 DO s 2* to s LOOP s ;
Capabilities and limitations:
- Support for locals referenced inside DO and FOR loops - OK
- Support for multiple {} uses in one definition - OK
- Support for TO and +TO to modify a local
- Locals mixed with raw return stack operations (
>R R>) - NOT OK - Locals defined inside a DO or FOR loop - NOT OK
- The low level ANSForth word
(LOCAL)is also supported.
Shell Utilities
Requires v7.0.7.3+ -- ONLY Posix + ESP32
cp ( "src" "dst" -- ) Copy "src" file to "dst". mv ( "src" "dst" -- ) Rename "src" file to "dst". rm ( "path" -- ) Remove "path" file. touch ( "path" -- ) Create "path" file if it doesn't exist. cat ( "path" -- ) Print contents of "path" file. ls ( "path" -- ) List files or directories in "path".
Requires v7.0.7.3+ -- ONLY Posix
cd ( "path" -- ) Change director to "path". mkdir ( "path" -- ) Create directory "path". rmdir ( "path" -- ) Remove directory "path". pwd ( -- ) Print current directory.
Visual Editor
Requires v7.0.7.2+
VISUAL EDIT ( "path" --) Enters a visual editor opening file "path".
NOTE: On ESP32 requires connection over an ANSI serial terminal like Putty.
LIMITATIONS: Terminal doesn't know screen dimensions
and is very redraw inefficient.
Keys:
Ctrl-S -- Save now.
Ctrl-X / Ctrl-Q -- Quit, asking Y/N to save.
Ctrl-L -- Redraw the screen.
Backspace -- Delete a character backwards.
Arrow Keys -- Movement.
PgUp/PgDn -- Scroll up/down a page.
Blocks
USE ( "name" -- ) Use "name" as the blockfile, e.g. USE /spiffs/foo OPEN-BLOCKS ( a n -- ) Open a file as the block file LOAD ( n -- ) Evaluate a block THRU ( a b -- ) Load blocks a thru b LIST ( n -- ) List a block BLOCK ( n -- a ) Get a 1024 byte block BUFFER ( n -- a ) Get a 1024 byte block without regard to old contents UPDATE ( -- ) Mark the last block modified FLUSH ( -- ) Save and empty all buffers EMPTY-BUFFERS ( -- ) Empty all buffers SAVE-BUFFERS ( -- ) Save all buffers SCR ( -- a ) Pointer to last listed block
Block Editor
These words are available inside theEDITOR vocabulary.
Note the block editor places newlines in the 63rd column of each line
to make the block file readable in a text editor.
WIPE ( -- ) Blank out the current block L ( -- ) List the current block D ( n -- ) Delete a line in the current block E ( n -- ) Clear a line in the current block R ( n "text" -- ) Replace a line in the current block A ( n "text" -- ) Add (insert) a line in the current block P ( -- ) Move to the previous block N ( -- ) Move to the next block
Sockets
Requires v7.0.7.2+ for UDP
These words are available inside thesockets vocabulary.
socket ( domain type protocol -- sock/err ) setsockopt ( sock level optname optval optlen -- 0/err ) bind ( sock addr addrlen -- 0/err ) listen ( sock connections -- 0/err ) sockaccept ( sock addr addrlen -- sock/err ) -- varies from bsd socks connect ( sock addr addrlen -- 0/err ) select ( numfds readfds writefds errfds timeout -- fd/err ) poll ( pollfds n timeout -- fd/err ) send ( sock a n flags -- n/err ) sendto ( sock a n flags addr addrlen -- n/err ) sendmsg ( sock msg flags -- n/err ) recv ( sock a n flags -- n/err ) recvfrom ( sock a n flags addr addrlen -- n/err ) recvmsg ( sock msg flags -- n/err ) gethostbyname ( hostnamez -- hostent/0 ) errno ( -- err ) -- ESP32 only as of v7.0.7.2 sockaddr ( "name" -- ) creates a sockaddr structure ->port@ ( a -- n ) get port from sockaddr ->port! ( n a -- ) set port in sockaddr ->addr@ ( a -- n ) get big-endian address from sockaddr ->addr! ( n a -- ) set big-endian address in sockaddr ip. ( n -- ) Print address as x.y.z.w IP address. ( Constants ) SOCK_STREAM SOCK_DGRAM SOCK_RAW AF_INET sizeof(sockaddr_in) SOL_SOCKET SO_REUSEADDR
Dictionary Images and Startup
WARNING: Danger ahead.
Snapshotting the dictionary may not be stable across reinstallations of the C build of Forth.
A collection of non-standard words is provided that allow snapshotting the dictionary and restoring it at startup, with a start word.
SAVE ( "name" -- ) Saves a snapshot of the current dictionary to a file.
RESTORE ( "name" -- ) Restore a snapshot from a file.
REMEMBER ( -- ) Save a snapshot to the default file
(./myforth or /spiffs/myforth on ESP32).
STARTUP: ( "name" -- ) Save a snapshot to the default file arranging for
"name" to be run on startup.
REVIVE ( -- ) Restore the default filename.
RESET ( -- ) Delete the default filename.
Here's an example usage:
: welcome ." Hello!" cr 100 0 do i . loop cr ; startup: welcome bye ( Next boot will run a custom startup message ) reset ( Reset removes the custom message )
The INTERNALS vocabulary has some additional words
for more control.
SAVE-NAME ( a n -- ) Save a snapshot if the current vocabulary to a file.
RESTORE-NAME ( a n -- ) Restore a snapshot from a file.
'COLD ( -- a ) Address of the word that will be run on startup.
REMEMBER-FILENAME ( -- a n ) Deferred word specifying the platform specific
default snapshot filename.
Web Interface
These words are inside theweb-interface vocabulary.
server ( port -- ) Start web UI on port (used to implement webui).
HTTP Daemon
Requires v7.0.6+
These words are inside thehttpd vocabulary.
server ( port -- ) Start an httpd on port. handleClient ( -- ) Get next request. path ( -- a n ) Request path, e.g. /foo method ( -- a n ) Request method, e.g. GET header ( a n -- a n ) Contents of header (or empty string). body ( -- a n ) Rquest body.
Telnet Daemon
These words are inside theweb-interface vocabulary.
server ( port -- ) Start telnet daemon on port.
ESP32forth Bindings
Because Arduino builds a statically linked image for flashing into ESP32 devices, all C function bindings need to be explicitly added. This is the current collection. Typically to reduce confusion, function names have be preserved even through verbose. In popular cases a shorted higher level name is provided.
See template.ino.
Allocation
These words are inside theinternals vocabulary.
MALLOC ( n -- a | 0 ) System malloc SYSFREE ( a -- ) System free REALLOC ( a n -- a | 0 ) System realloc
Serial
These words are inside theSerial vocabulary.
Serial.begin ( baud -- ) Start serial port Serial.end ( -- ) End serial port Serial.available ( -- f ) Is serial data available Serial.readBytes ( a n -- n ) Read serial bytes, return number gotten Serial.write ( a n -- n ) Write serial bytes Serial.flush ( -- ) Flush serial buffer
Serial Bluetooth
These words are inside thebluetooth vocabulary.
NOTE: Starting in v7.0.7.13 the optional module serial-bluetooth.h must be placed next to ESP32forth.ino to include this capability.
SerialBT.new ( -- bt ) Allocate new BT object SerialBT.delete ( bt -- ) Free BT object SerialBT.begin ( localname ismaster bt -- f ) SerialBT.end ( bt -- ) SerialBT.available ( bt -- f ) SerialBT.readBytes ( a n bt -- n ) SerialBT.write ( a n bt -- n ) SerialBT.flush ( bt -- ) SerialBT.hasClient ( bt -- f ) SerialBT.enableSSP ( bt -- ) SerialBT.setPin ( z bt -- f ) SerialBT.unpairDevice ( addr bt -- f ) SerialBT.connect ( remotename bt -- f ) SerialBT.connectAddr ( addr bt -- f ) SerialBT.disconnect ( bt -- f ) SerialBT.connected ( timeout bt -- f ) SerialBT.isReady ( checkMaster timeout -- f ) Default checkMaster=false, timeout=0
Bluetooth
These words are inside thebluetooth vocabulary.
esp_bt_dev_get_address ( -- a ) addr of 6 byte mac address
GPIO
pinMode ( pin mode -- ) Set GPIO pin mode digitalWrite ( pin value -- ) Set GPIO pin state analogRead ( pin -- n ) Analog read from 0-4095 pulseIn ( pin value usec -- usec/0 ) Wait for a pulseAvailable on devices other than ESP32-C3:
dacWrite ( pin 0-255 -- ) Write to DAC (pin 25, 26)
ledc
These words are inside theledc vocabulary.
(arduino-esp32 3.x+) ledcAttach ( pin freq resolution -- f ) ledcAttachChannel ( pin freq resolution channel -- f ) ledcDetach ( pin -- f ) ledcRead ( channel -- n ) ledcReadFreq ( channel -- freq ) ledcWrite ( channel duty -- ) ledcWriteTone ( channel freq -- freq ) ledcWriteNote ( channel note octave -- freq ) ledcChangeFrequency ( pin freq resolution -- freq )If built with arduino-esp32 2.x, this is the interface:
(arduino-esp32 2.x+) ledcSetup ( channel freq resolution -- freq ) ledcAttachPin ( pin channel -- ) ledcDetachPin ( pin -- ) ledcRead ( channel -- n ) ledcReadFreq ( channel -- freq ) Get frequency (x 1,000,000) ledcWrite ( channel duty -- ) ledcWriteTone ( channel freq ) Write tone frequency (x 1000) ledcWriteNote ( channel note octave -- freq )
Short GPIO Names
pin ( value pin# -- ) Set GPIO pin value adc ( pin# -- n ) Analog read pin, result 0-1023
System
MS ( n -- ) Pause for some number of milliseconds. MS-TICKS ( -- n ) Time since start in milliseconds. TERMINATE ( n -- ) Call system exit.
Files
R/O ( -- mode ) R/W ( -- mode ) W/O ( -- mode ) BIN ( mode -- mode ) CLOSE-FILE ( fh -- ior ) OPEN-FILE ( a n mode -- fh ior ) CREATE-FILE ( a n mode -- fh ior ) DELETE-FILE ( a n -- ior ) WRITE-FILE ( a n fh -- ior ) READ-FILE ( a n fh -- n ior ) FILE-POSITION ( fh -- n ior ) REPOSITION-FILE ( n fh -- ior ) FILE-SIZE ( fh -- n ior )
WiFi
These words are inside theWiFi vocabulary.
WiFi.config ( ip gateway subnet dns -- ) Packaged a.b.c.d little-endian Wifi.begin ( ssid-z password-z -- ) Wifi.disconnect ( -- ) WiFi.status ( -- n ) WiFi.macAddress ( a -- ) WiFi.localIP ( -- ip ) WiFi.gatewayIP ( -- ip ) WiFi.subnetMask ( -- ip ) WiFi.mode ( mode -- ) WIFI_MODE_NULL WIFI_MODE_STA WIFI_MODE_AP WIFI_MODE_APSTA WiFi.setTxPower ( powerx4 -- ) Set power x4 WiFi.getTxPower ( -- powerx4 ) Get power x4 ( In 7.0.6.17 and up ) WiFi.softAP ( ssid password/0 -- success ) WiFi.softAPIP ( -- ip ) WiFi.softAPBroadcastIP ( -- ip ) WiFi.softAPNetworkID ( -- ip ) WiFi.softAPConfig ( localip gateway subnet -- success ) WiFi.softAPdisconnect ( wifioff -- success ) WiFi.softAPgetStationNum ( -- num )
mDNS
MDNS.begin ( hostname-z -- f ) Start multicast dns
MDNS.setInstanceName ( name-z -- ) Set the instance (friendly) name
MDNS.addService ( service-z protocol-z port-n -- f ) Advertise a service (such as "http") using a protocol ("tcp" or "udp") and a port number.
MDNS.addServiceTxt ( service-z protocol-z key-z value-z -- ) Add a service key/value pair
SPIFFS
These words are inside theSPIFFS vocabulary.
SPIFFS.begin ( format-on-fail path-z max-files -- f ) SPIFFS.end ( -- ) SPIFFS.format ( -- f ) SPIFFS.totalBytes ( -- n ) SPIFFS.usedBytes ( -- n )
WebServer (DEPRECATED)
These words are inside theWebServer vocabulary.
Removed in 7.0.6.14, use httpd instead.
WebServer.new ( port -- ws ) Allocate new webserver object WebServer.delete ( ws -- ) Delete webserver object WebServer.begin ( port ws -- ) WebServer.stop ( ws -- ) WebServer.on ( path-z xt ws -- ) Set up a web path handle callback WebServer.handleClient ( ws -- ) Handle one client request WebServer.hasArg ( z ws -- f ) By name WebServer.arg ( z ws -- z ) By name WebServer.argi ( n ws -- z ) By index WebServer.argName ( n ws -- z) By index WebServer.args ( ws -- n ) Number of args WebServer.setContentLength ( n ws -- ) WebServer.sendHeader ( name-z value-z fist ws -- ) WebServer.send ( code mimetype data ws -- ) WebServer.sendContent ( z ws -- ) WebServer.method ( ws -- n ) GET / POST etc.
httpd
These words are inside thehttpd vocabulary.
server ( port -- ) Run a webserver on a port (in background, returns immediately).
handleClient ( -- f ) Wait for a client to connect, true if connected.
path ( -- a n ) Get request path.
method ( -- a n ) Get request method (GET/POST).
header ( a n -- a n ) Get header value or empty string.
body ( -- a n ) Get request body.
response ( mime mime# result result# status -- ) Respond with a particular mime type result and status.
ok-response ( mime mime# ) Response with a HTTP 200.
bad-response ( -- ) Response with HTTP 400 Bad request.
notfound-response ( -- ) Response with HTTP 404 Not found.
send ( a n -- ) Send response bytes.
NOTE: You may want to use this feature in tandem with tasks / streams.
Example:
also httpd
: handle-index
s" text/html" ok-response r|
Hi!
| send ;
: handle1
." Got a request for: " path type cr
path s" /" str= if handle-index exit then
notfound-response
;
: run 8080 server
begin handleClient if handle1 then pause again ;
run
Wire
These words are inside theWire vocabulary.
Wire.begin ( -- f ) Wire.setPins ( sda scl -- f ) Wire.setClock ( frequency -- ) Wire.getClock ( -- frequency ) Wire.setTimeout ( ms -- ) Default is 50ms Wire.getTimeout ( -- ms ) Wire.beginTransmission ( n -- ) Wire.endTransmission ( sendstop -- f ) Default is true Wire.requestFrom ( address quantity sendstop -- n ) Wire.write ( a n -- n ) Wire.available ( -- f ) Wire.read ( -- ch ) Wire.peek ( -- ch ) Wire.flush ( -- )These words were available in v7.0.6.5 and before, but are now deprecated as the underlying Arduino functions have gone away in the v2.0.1 ESP32 Arduino library.
Wire.lastError ( -- n ) Wire.getErrorText ( n -- z ) Wire.busy ( -- f ) Wire.writeTransmission ( addr a n sendstop -- err ) Wire.readTransmission ( addr a n sendstop acount -- err )
SD
These words are inside theSD vocabulary.
They allow use of an SDcard over SPI.
SD.begin ( -- ok ) uses all the defaults "/sd" etc.
SD.beginDefaults ( -- sspin SPIClass frequency mountpointsz maxfiles format_if_empty )
( SS SPI 4000000 "/sd" 5 false )
SD.beginFull ( sspin SPIClass frequency mountpoint maxfiles format_if_empty -- ok )
SD.end ( -- )
SD.cardType ( -- n )
SD.totalBytes ( -- n )
SD.usedBytes ( -- n )
SD_MMC
These words are inside theSD_MMC vocabulary.
They allow use of an SDcard over MMC internal interface.
Note, SD_MMC is unavailable on ESP32-S2 and ESP32-C3.
SD_MMC.begin ( -- ok ) uses all the defaults "/sdcard" etc.
SD_MMC.beginDefaults ( -- mountsz mode1bit format_if_fail )
( "/sdcard" false false )
( sdmmc_freq not supported for generality )
SD_MMC.beginFull ( mountsz mode1bit format_if_fail -- ok )
SD_MMC.end ( -- )
SD_MMC.cardType ( -- n )
SD_MMC.totalBytes ( -- n )
SD_MMC.usedBytes ( -- n )
SD_MMC.setPins ( clk cmd d0 d1 d2 d3 -- f ) v7.0.7.20 and up
Tasks
These words are inside theTASKS vocabulary.
PAUSE ( -- ) Yield to other tasks.
MS ( n -- ) Pause for some number of milliseconds (yields to other tasks).
TASK ( xt dsz rsz "name" -- ) Create a new task with dsz size data stack
and rsz size return stack running xt.
START-TASK ( task -- ) Activate a task.
.TASKS ( -- ) List running tasks.
Example:
tasks
: hi begin ." Time is: " ms-ticks . cr 1000 ms again ;
' hi 100 100 task my-counter
my-counter start-task
RTOS
These words are inside theRTOS vocabulary.
xPortGetCoreID ( -- n ) xTaskCreatePinnedToCore ( fn name stack-depth params priority taskout coreid -- ) vTaskDelete ( task ) -- )
ESP32 WebUI
A terminal over the web can be activated. Contact at port printed or via mDNS http://forth/.
webui ( network-z password-z -- ) login and start webui login ( network-z password-z -- ) login to wifi only
Usage:
z" NETWORK-NAME" z" PASSWORD" webui
See web_interface.fs.
Autoexec.fs
NOTE: This section describes one mechanism for running code at startup. See this for an alternate option.
The system will automatically attempt to mount SPIFFS filesystem at /spiffs.
It will then at start attempt to load /spiffs/autoexec.fs
One way this feature can be used to configure the Web UI to start by default. When doing this, be sure to test your Web UI settings work well first.
r| z" NETWORK-NAME" z" PASSWORD" webui | s" /spiffs/autoexec.fs" dump-file
To remove a previously configured autoexec.fs you will need
to be able to reboot in a mode with Forth. One way to do this is to search
for the line in the .ino file that refers to autoexec.fs
and replace it with a different name. Then run the following:
s" /spiffs/autoexec.fs" delete-file
See autoboot.fs.
ESP32forth Optional Modules
Several optional modules are now available in the optional/
directory next to ESP32forth.ino. To use these modules,
move them up a directory to be adjacent to ESP32forth.ino.
SPI Flash
These words are inside thespi_flash vocabulary.
NOTE: Starting in v7.0.7.13 the optional module spi-flash.h must be placed next to ESP32forth.ino to include this capability.
NOTE: Recent versions of Arduino tools seem to be incompatible with this interface, this module is now deprecated.
spi_flash_init ( -- ) Init driver access. spi_flash_get_chip_size ( -- n ) Get flash size. spi_flash_erase_sector ( sector -- err ) Erase a sector. spi_flash_erase_range ( addr size -- err ) Erase a range. spi_flash_write ( destaddr src size -- err ) Write to flash. spi_flash_write_encrypted ( destaddr src size -- err ) Write encrypted. spi_flash_read ( srcaddr dst size -- err ) Read from flash. spi_flash_read_encrypted ( srcaddr dst size -- err ) Read encrypted. spi_flash_mmap ( srcaddr size memtype out outhandle -- err ) Map region. spi_flash_mmap_pages ( pages pages# memtype out outhandle -- err ) Map pages. spi_flash_munmap ( handle -- ) Unmap region. spi_flash_mmap_dump ( -- ) Dump memory map. spi_flash_mmap_get_free_pages ( memtype -- n ) Get free pages. spi_flash_cache2phys ( a -- addr ) Get flash addr. spi_flash_phys2cache ( addr memtype -- a ) Get mapped flash addr. spi_flash_cache_enabled ( -- f ) Is flash enabled. esp_partition_t_size ( -- n ) sizeof(esp_parition_t). esp_partition_find ( type subtype szlabel -- it ) Get partition iterator. esp_partition_find_first ( type subtype szlabel -- part ) Get first partition. esp_partition_get ( it -- part ) Get current partition. esp_partition_next ( it -- it' ) Get next partition. esp_partition_iterator_release ( it -- ) Free iterator. esp_partition_verify ( part -- part' ) Verify partition. esp_partition_read ( part srcoff dst size -- err ) Read from partition. esp_partition_write ( part dstoff src size -- err ) Write to partition. esp_partition_erase_range ( part start size -- err ) Erase range. esp_partition_mmap ( part off size memtype out outhandle -- err ) Map memory. esp_partition_get_sha256 ( part a -- err ) Get sha256 digest. esp_partition_check_identity ( part part -- f ) Check partitions for equality.
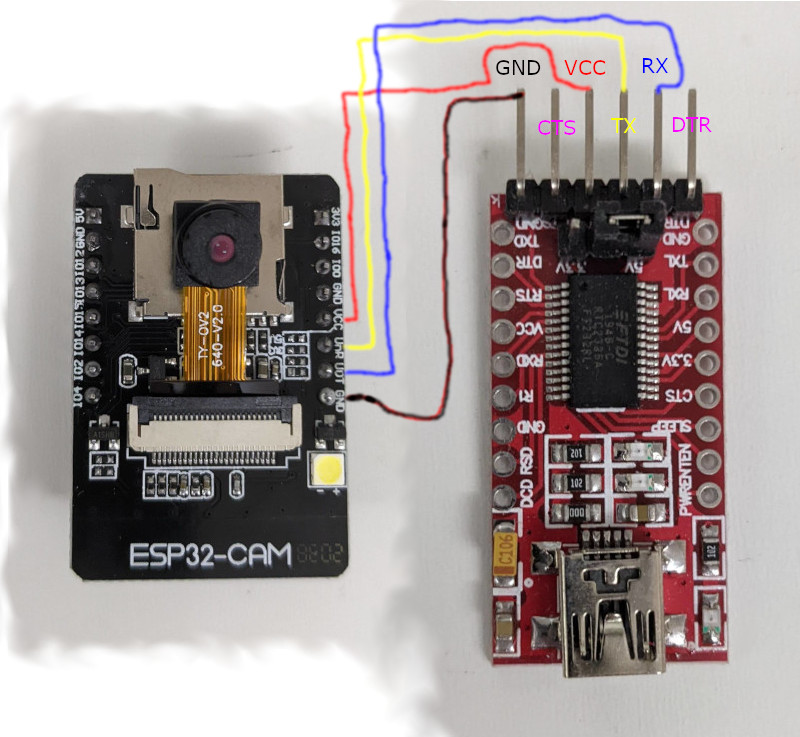
Camera
These words are inside thecamera vocabulary.
NOTE: Starting in v7.0.7.13 the optional module camera.h must be placed next to ESP32forth.ino to include this capability.
esp_camera_init ( config -- f ) esp_camera_deinit ( -- f ) esp_camera_fb_get ( -- fb ) esp_camera_fb_return ( fb -- ) esp_camera_sensor_get ( -- sensor ) esp_camera_save_to_nvs ( key -- n ) esp_camera_load_from_nvs ( key -- n ) ( formats ) PIXFORMAT_RGB565 PIXFORMAT_YUV422 PIXFORMAT_GRAYSCALE PIXFORMAT_JPEG PIXFORMAT_RGB888 PIXFORMAT_RAW PIXFORMAT_RGB444 PIXFORMAT_RGB555 ( frame sizes ) FRAMESIZE_96x96 ( 96x96) FRAMESIZE_QQVGA ( 160x120 ) FRAMESIZE_QCIF ( 176x144 ) FRAMESIZE_HQVGA ( 240x176 ) FRAMESIZE_240x240 ( 176x144 ) FRAMESIZE_QVGA ( 320x240 ) FRAMESIZE_CIF ( 400x296 ) FRAMESIZE_HVGA ( 480x320 ) FRAMESIZE_VGA ( 640x480 ) FRAMESIZE_SVGA ( 800x600 ) FRAMESIZE_XGA ( 1024x768 ) FRAMESIZE_HD ( 1280x720 ) FRAMESIZE_SXGA ( 1280x1024 ) FRAMESIZE_UXGA ( 1600x1200 ) ( access to config ) camera-fb-count ( -- a ) camera-jpeg-quality ( -- a ) camera-frame-size ( -- a ) camera-format ( -- a ) ( Access a frame returned by esp_camera_fb_get ) fb->buf ( -- a ) fb->len ( -- n ) fb->width ( -- n ) fb->height ( -- n ) fb->format ( -- n ) fb->sec ( -- n ) fb->usec ( -- n ) ( Access methods in struct returned by esp_camera_sensor_get ) s->xclk_freq_hz ( a ) s->init_status ( s ) s->reset ( s ) s->set_pixformat ( s pixformat ) s->set_framesize ( s framesize ) s->set_contrast ( s level ) s->set_brightness ( s level ) s->set_saturation ( s level ) s->set_sharpness ( s level ) s->set_denoise ( s level ) s->set_gainceiling ( s gainceil ) s->set_quality ( s quality ) s->set_colorbar ( s enable ) s->set_whitebal ( s enable ) s->set_gain_ctrl ( s enable ) s->set_exposure_ctrl ( s enable ) s->set_hmirror ( s enable ) s->set_vflip ( s enable ) ( --- ) s->set_aec2 ( s enable ) s->set_awb_gain ( s enable ) s->set_agc_gain ( s gain ) s->set_aec_value ( s gain ) ( --- ) s->set_special_effect ( s effect ) s->set_wb_mode ( s mode ) s->set_ae_level ( s level ) ( --- ) s->set_raw_gma ( s enable ) s->set_lenc ( s enable ) ( --- ) s->get_reg ( s reg mask ) s->set_reg ( s reg mask value ) s->set_res_raw ( s startX startY endX endY offsetX offsetY totalX totalY outputX outputY scale binning ) s->set_pll ( s bypass mul sys root pre seld5 pclken pclk ) s->set_xclk ( s time xclk )
Camera Server
Requires v7.0.6+
WIP Prototype - Not yet stableThese words are inside the
camera-server vocabulary.
server ( port -- ) Start an image server at port,
e.g. http://IP/image will produce an image
Interrupts
These words are inside theINTERRUPTS vocabulary.
NOTE: Starting in v7.0.7.15 the optional module interrupts.h must be placed next to ESP32forth.ino to include this capability.
High Level words:
pinchange ( xt pin -- ) Call xt when pin changes.
Example:
17 input pinMode : test ." pinvalue: " 17 digitalRead . cr ; ' test 17 pinchange
Low Level words:
ESP_INTR_FLAG_DEFAULT -- Default handler allows per pin routing Various triggers: #GPIO_INTR_DISABLE #GPIO_INTR_POSEDGE #GPIO_INTR_NEGEDGE #GPIO_INTR_ANYEDGE #GPIO_INTR_LOW_LEVEL #GPIO_INTR_HIGH_LEVEL gpio_config ( gpio_config_t* -- 0/err ) gpio_reset_pin ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_set_intr_type ( pin type -- 0/err ) gpio_intr_enable ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_intr_disable ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_set_level ( pin level -- 0/err ) gpio_get_level ( pin -- level ) gpio_set_direction ( pin mode -- 0/err ) gpio_set_pull_mode ( pin mode -- 0/err ) gpio_wakeup_enable ( pin type -- 0/err ) gpio_wakeup_disable ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_pullup_en ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_pullup_dis ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_pulldown_en ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_pulldown_dis ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_hold_en ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_hold_dis ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_deep_sleep_hold_en ( -- ) gpio_deep_sleep_hold_dis ( -- ) gpio_install_isr_service ( a -- ) Typically ESP_INTR_FLAG_DEFAULT gpio_uninstall_isr_service gpio_isr_handler_add ( pin xt arg -- 0/err ) gpio_isr_handler_remove ( pin -- 0/err ) gpio_set_drive_capability ( pin cap -- 0/err ) gpio_get_drive_capability ( pin cap* -- 0/err ) esp_intr_alloc ( source flags xt args handle* -- 0/err ) esp_intr_free ( handle -- 0/err )
Timers
These words are inside thetimers vocabulary.
timer_isr_callback_add ( group timer xt arg -- 0/err ) Register a raw timer ISR callback. timer_isr_register ( group timer xt arg ret -- 0/err ) REMOVED
RMT
These words are inside theRMT vocabulary.
NOTE: Starting in v7.0.7.15 the optional module rmt.h must be placed next to ESP32forth.ino to include this capability.
rmt_set_clk_div ( channel div8 -- err ) rmt_get_clk_div ( channel @div8 -- err ) rmt_set_rx_idle_thresh ( channel thresh16 -- err ) rmt_get_rx_idle_thresh ( channel @thresh16 -- err ) rmt_set_mem_block_num ( channel memnum8 -- err ) rmt_get_mem_block_num ( channel @memnum8 -- err ) rmt_set_tx_carrier ( channel enable highlev lowlev carrierlev -- err ) rmt_set_mem_pd ( channel f -- err ) rmt_get_mem_pd ( channel @f -- err ) rmt_tx_start ( channel f -- err ) rmt_tx_stop ( channel -- err ) rmt_rx_start ( channel f -- err ) rmt_rx_stop ( channel -- err ) rmt_tx_memory_reset ( channel -- err ) rmt_rx_memory_reset ( channel -- err ) rmt_set_memory_owner ( channel owner -- err ) rmt_get_memory_owner ( channel @owner -- err ) rmt_set_tx_loop_mode ( channel f -- err ) rmt_get_tx_loop_mode ( channel @f -- err ) rmt_set_rx_filter ( channel enable thresh8 -- err ) rmt_set_source_clk ( channel baseclk -- err ) rmt_get_source_clk ( channel @baseclk -- err ) rmt_set_idle_level ( channel enable level -- err ) rmt_get_idle_level ( channel @enable @level -- err ) rmt_get_status ( channel @status -- err ) rmt_set_rx_intr_en ( channel enable -- err ) rmt_set_err_intr_en ( channel enable -- err ) rmt_set_tx_intr_en ( channel enable -- err ) rmt_set_tx_thr_intr_en (channel enable thresh -- err ) rmt_set_gpio ( channel mode gpio# invertsig -- err ) rmt_config ( rmt_config_t* ) rmt_isr_register ( fn arg allocflags handle -- err ) rmt_isr_deregister ( handle -- err ) rmt_fill_tx_items ( channel @items items# offset -- err ) rmt_driver_install ( channel rxbufsize allocflags -- err ) rmt_driver_uinstall ( channel -- err ) rmt_get_channel_status ( channel @status -- err ) rmt_get_counter_clock ( channel @clockhz -- err ) rmt_write_items ( channel @items items# wait -- err ) rmt_wait_tx_done ( channel time -- err ) rmt_get_ringbuf_handle ( channel @handle -- err ) rmt_translator_init ( channel fn -- err ) rmt_translator_set_context ( channel @context -- err ) rmt_translator_get_context ( channel @@context -- err ) rmt_write_sample ( channel src src# wait -- err ) rmt_register_tx_end_callback --- NOT SUPPORTED rmt_memory_rw_rst --- DEPRECATED USE rmt_tx_memory_reset or rmt_rx_memory_reset rmt_set_intr_enable_mask --- DEPRECATED interrupt handled by driver rmt_clr_intr_enable_mask --- DEPRECATED interrupt handled by driver rmt_set_pin --- DEPRECATED use rmt_set_gpio instead
HTTPClient
These words are inside the optionalHTTPClient vocabulary.
NOTE: This vocabulary is optional, available by placing http-client.h next to ESP32forth.ino to include this capability.
NetworkClientSecure.new ( -- a ) Create a new secure client (for HTTPS) NetworkClientSecure.delete ( a -- ) Delete a secure client NetworkClientSecure.setCACert ( cacertz nc -- ) Set a CACert (cstring) for a secure client HTTPClient.new ( -- a ) Create a new HTTPClient session HTTPClient.delete ( a -- ) Delete an HTTPClient HTTPClient.begin ( urlz hc -- f ) Begin an HTTP session with a url HTTPClient.beginNC ( urlz nc hc -- f ) Begin an HTTPS session with a url and secure client HTTPClient.end ( hc -- ) End an HTTP/S session HTTPClient.connected ( hc -- f ) Check if a session is connected HTTPClient.setReuse ( f hc -- ) Set if session keep-alive is enabled HTTPClient.setUserAgent ( agentz hc -- ) Set user-agent string HTTPClient.setAuthorization ( username password hc -- ) Set an authorization HTTPClient.setFolowRedirects ( f hc -- ) Set if redirects can be followed HTTPClient.setRedirectLimit ( n hc -- ) Set number of allowed redirects HTTPClient.GET ( hc -- n ) Start a GET, return http code HTTPClient.POST ( a n hc -- n ) Start a POST, with a data payload, return http code HTTPClient.addHeader ( key value hc -- ) Set an HTTP header HTTPClient.sendRequest ( methodz a n hc -- n ) Send a request with arbitrary method, payload HTTPClient.getSize ( hc -- n ) Get size of response HTTPClient.getString ( a n hc -- n ) Read result into a buffer HTTPClient.getStreamPtr ( hc -- stream ) Get the result as a stream NetworkClient.available ( stream -- n ) Get number of bytes available NetworkClient.readBytes ( a n stream -- n ) Read into a buffer
Timers
These words are inside theTIMERS vocabulary.
NOTE: Starting in v7.0.7.15 the optional module interrupts.h must be placed next to ESP32forth.ino to include this capability.
NOTE: These are low level ESP32 timers. For a periodic background operation, you'll probably want to use TASKS.
High Level words:
( timer t = 0-3 ) interval ( xt usec t -- ) Setup timer t to call xt each after usec rerun ( t -- ) REMOVED - rerun no longer required as autoreload used
NOTE: The Interrupt Watchdog timer doesn't work well with use of serial output during an interrupt routine. Operations durring the handler should be kept to a minimum.
Example: timers variable x : hi 1 x +! ; ' hi 1000000 0 interval ( run hi every second ) x @ . ( See value of x goes up )
Medium Level words:
timer@ ( t -- lo hi ) Get timer counter current value timer! ( lo hi t -- ) Set timer counter current value alarm@ ( t -- lo hi ) Get alarm value alarm! ( lo hi t -- ) Set alarm value enable! ( f t -- ) Timer enable/disable increase! ( f t -- ) Timer increasing/decreasing divider! ( n t -- ) Timer divider 2 - 65535 alarm-enable! ( f t -- ) Enable/disable alarm. int-enable! ( f t -- ) Enable/disble interrupt. onalarm ( xt t -- ) Set callback alarm ( t -- a ) REMOVED alarm-enable@ ( t -- f ) REMOVED
Low Level words:
( group n = 0/1, timer x = 0/1, watchdog m = 0-5 ) TIMGn_TxCONFIG_REG ( n x -- a ) TIMGn_TxLOHI_REG ( n x -- a ) TIMGn_TxUPDATE_REG ( n x -- a ) TIMGn_TxALARMLOHI_REG ( n x -- a ) TIMGn_TxLOADLOHI_REG ( n x -- a ) TIMGn_TxLOAD_REG ( n x -- a ) TIMGn_Tx_WDTCONFIGm_REG ( n m -- a ) TIMGn_Tx_WDTFEED_REG ( n -- a ) TIMGn_Tx_WDTWPROTECT_REG ( n -- a ) TIMGn_RTCCALICFG_REG ( n -- a ) TIMGn_RTCCALICFG1_REG ( n -- a ) TIMGn_Tx_INT_ENA_REG ( n -- a ) TIMGn_Tx_INT_RAW_REG ( n -- a ) TIMGn_Tx_INT_ST_REG ( n -- a ) TIMGn_Tx_INT_CLR_REG ( n -- a )
ESPNOW
These words are inside theespnow vocabulary.
NOTE: The optional module espnow.h must be placed next to ESP32forth.ino to include this capability.
espnow_init ( -- err ) espnow_deinit ( -- err ) espnow_add_peer ( a -- err ) espnow_send ( b2 b1 n0 -- err ) ( Constants ) ESP_OK ESP_FAIL ESP_ERR_NO_MEM \ Out of memory ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG \ Invalid argument ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE \ Invalid state ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE \ Invalid size ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND \ Requested resource not found ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED \ Operation or feature not supported ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT \ Operation timed out ESP_ERR_INVALID_RESPONSE \ Received response was invalid ESP_ERR_INVALID_CRC \ CRC or checksum was invalid ESP_ERR_INVALID_VERSION \ Version was invalid ESP_ERR_INVALID_MAC \ MAC address was invalid ESP_ERR_NOT_FINISHED \ Operation has not fully completed
Adding Words
Words can be added based on C functions by placing a file named userwords.h
alongside the .ino file for ESP32forth.
Requires v7.0.6.4+
Before v7.0.6.4, user words required editing the .ino file.
Because of the use of X-Macros words can be
added in as little as one line. Locate the macro called PLATFORM_OPCODE_LIST
and add your words there.
NOTE: Be careful to end each line with a \ so the macros will chain correctly.
To add a word containing only letters, numbers, and underscore you can use Y.
---- userwords.h ---- #define USER_WORDS \ Y(MY_WORD123, c_function_to_call()) \
If your word name contains other characters, instead use X.
You will need to make up an alternate name for the middle parameter.
It must contain only letters, numbers, and underscore.
The name is not used anywhere else, but must be unique.
---- userwords.h ----
#define USER_WORDS \
X("myword!", MY_WORD_BANG, c_function_to_call()) \
Values from the data stack can be accessed via
the variables tos (Top of Stack) and
sp (Pointer to the rest of the stack).
The stack has the data type cell_t.
You can push a value of any type to the stack with the macro PUSH:
---- userwords.h ---- #define USER_WORDS \ Y(MY_WORD, PUSH calculate_magic_value()) \
To simplify calling C functions, you can also refer to elements on the stack with the types positional names:
n10 n9 n8 n7 n6 n5 n4 n3 n2 n1 n0 - Access stack as cell_t integer values
c4 c3 c2 c1 c0 - Access stack as char* values
b4 b3 b2 b1 b0 - Access stack as uint8_t* byte values
a6 a5 a4 a3 a2 a1 a0 - Access stack as void* values
Examples:
---- userwords.h ----
void send_message(const char *message, int code);
...
#define USER_WORDS \
X("send-message", SEND_MESSAGE, send_message(c1, n0)) \
You can always replace the top item on the stack with SET:
---- userwords.h ---- #define USER_WORDS \ Y(DECODE, SET decode_func(n0)) \
You can drop elements from the stack with DROP
or DROPn(number).
You can nip elements from below top of the stack with NIP
or NIPn(number).
Be aware that like PUSH this will cause stack indices to change.
---- userwords.h ---- int my_cool_function(char *foo, int bar, uint8_t *baz); ... #define USER_WORDS \ Y(MY_FUNC, n0 = my_cool_function(c2, n1, b0); NIPn(2)) \
Multiple C statements can be included in the code area of a word, but care must be taken to generally avoid {}s. If you find you need nesting, a separate function is recommended.
New variables can be declared in each word and are scoped to that word.
---- userwords.h ----
#define USER_WORDS \
Y(MY_WORD, cell_t foo = n0; DROP; char *x = c0; DROP; \
PUSH my_func(foo, x)) \